4. Operators¶
In this section we’ll have a closer look at operators in Python. Operators are used to perform operations on variables and values. Python divides operators in the following groups:
Arithmetic operators
Assignment operators
Comparison operators
Logical operators
Identity operators
Membership operators
Bitwise operators
We’ll have a look at all of them except bitwise operators as they are out of scope for this training session.
4.1. Arithmetic Operators¶
Arithmetic operators are used (as the name suggests) to perform arithmetical operations on numeric variables and values (e.g. int and float).
Note: Some of these arithmetic operators are implemented for more complex data structures like lists or dictionaries. However, they have a different meaning than the once discussed here.
| Operator | Name | Example |
|---|---|---|
| + | Addition | x + y |
| - | Subtraction | x - y |
| * | Multiplication | x * y |
| / | Division | x / y |
| % | Modulus | x % y |
| ** | Exponentiation | x ** y |
| // | Floor division | x // y |
The following code section shows you, how you could use the operators listed above.
>>> x = 5
>>> y = 3
>>> x + 2
7
>>> x + y
8
>>> x * y
15
>>> 7 / 2 # always results in a float
3.5
>>> 7 // 2 # floor-division always results in an integer
3
>>> 7 % 2 # modulo operation -> returns the remainder of a division
1
>>> 7 ** 2 # square number of 7
49
4.2. Assignment Operators¶
Assignment operators are used to create or override variables.
Besides the normal assignment operator =, which is used in the Variables section, there exist other assignment operators, which are a combination of the assignment operator and an arithmetical operator.
| Operator | Example | Same As |
|---|---|---|
| = | x = 5 | x = 5 |
| += | x += 3 | x = x + 3 |
| -= | x -= 3 | x = x - 3 |
| *= | x *= 3 | x = x * 3 |
| /= | x /= 3 | x = x / 3 |
| %= | x %= 3 | x = x % 3 |
| **= | x **= 3 | x = x ** 3 |
| //= | x //= 3 | x = x // 3 |
>>> x = 5
>>> x += 3
>>> x
8
>>> x %= 2
>>> x
0
4.3. Comparison Operators¶
Comparison operators are used to compare certain values (or variables) and get back a boolean value. Let’s assume we have two variables and want to know, whether they are equal or not:
>>> x = 3
>>> y = 6
>>> x == y
False
>>> x != y
True
>>> x < y
True
Below you’ll find a list of available comparison operators.
| Operator | Name | Example |
|---|---|---|
| == | Equal | x == y |
| != | Not equal | x != y |
| > | Greater than | x > y |
| < | Less than | x < y |
| >= | Greater than or equal to | x >= y |
| <= | Less than or equal to | x <= y |
4.4. Logical Operators¶
Logical operators are used to connect booleans logically to see, whether they are True or False within a certain context.
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| and | Returns True if both statements are true | x < 5 and x < 10 |
| or | Returns True if one of the statements is true | x < 5 or x < 4 |
| not | Reverse the result, returns False if the result is true | not(x < 5 and x < 10) |
>>> x = 3 == 3
>>> x
True
>>> y = 4 < 3
>>> y
False
>>> x and y
False
>>> x and not y
True
>>> x or y
True
4.5. Identity Operators¶
Identity operators are used to check the identity of an object.
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| is | Returns true if both variables are the same object | x is y |
| is not | Returns true if both variables are not the same object | x is not y |
Note: Checking whether a value is
None(equivalent tonullin C or Java) is performed by using the identity operatorisand not using the comparison operator==.
>>> x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
>>> y = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
>>> x is y
False
>>> x is not y
True
>>> y = x
>>> x is y
True
The following diagram illustrates, what happended in the example provided above.
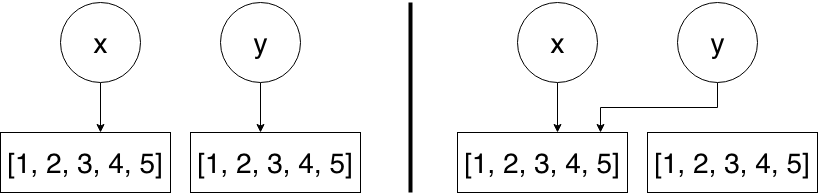
On the left-hand side you can see, that both variables point to independent lists.
However, when we set y = x, y points to the same list as x, which you can see on the right-hand side.
4.6. Membership Operators¶
With membership operators you can check, whether a certain sequence is present in an object.
For instance you could check if the number 5 is part of a list of grades or if the name Felix contains the letter p.
>>> grades = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
>>> grades
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
>>> 5 in grades
True
>>> name = "Felix"
>>> name
'Felix'
>>> "p" in name
False
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| in | Returns True if a sequence with the specified value is present in the object | x in y |
| not in | Returns True if a sequence with the specified value is not present in the object | x not in y |